Photorec For Mac
Posted : admin On 10/29/2019ICare only operates on Windows, not on Mac. The scanning really takes a long time. PhotoRec Data Recovery. PhotoRec is one of best SD card recovery freeware that recover all types of files. It is 100% free for SD card data recovery, but operating this software itself is a difficult task. It will take users a lot of time to get the hang. PhotoRec is a free and open-source utility software for data recovery with text-based user interface using data carving techniques, designed to recover lost files from various digital camera memory, hard disk and CD-ROM. PhotoRec is a free and open-source utility software for data recovery with text-based user interface using data carving techniques, designed to recover lost files from various digital camera memory, hard disk and CD-ROM.It can recover the files with more than 480 file extensions (about 300 file families). It is also possible to add custom file signature to detect less known files.
PhotoRec for Mac, free and safe download. PhotoRec latest version: Free, simple photo retrieval with PhotoRec. PhotoRec is a free digital photo recovery tool that.
Download PhotoRec Latest Version for Windows, Mac & Linux – PhotoRec is a portable software that doesn’t need to install it first. TestDisk has two applications in it, TestDisk itself and this app. This is the explanation:
- TestDisk: This tool can find FAT32, NTFS, or ReiserFS partitions that are deleted and restore them. Be careful, besides changing the Master Boot Record (MBR), TestDisk can also overwrite partitions that are not damaged. Run ‘tesdisk_win.exe’. Under ‘Select a media’, select the hard disk with the corresponding partition. Confirm your choice by clicking ‘Proceed’. The tool will ask for ‘partition table type’ for the PC type is ‘Intel’. Next, choose ‘Analyze’. The tool scans the hard disk and looks for all entries in the MBR, including lost partitions.
After TestDisk displays the results, you can change the attributes of a partition, for example from ‘D’ to deleted to ‘L’ to logical. To find deleted partitions, which are no longer listed there, Advanced Search is available. You can change the attribute again and overwrite the MBR with the ‘Write’ command.
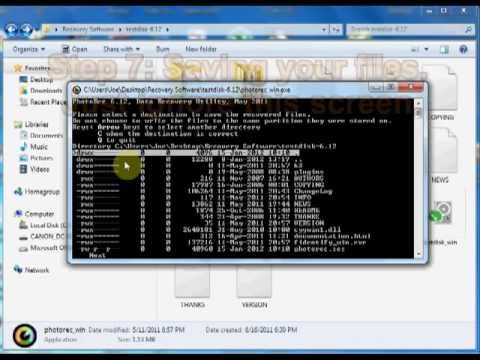
- PhotoRec: This software specializes in restoring deleted photos, but it can also save other types of files such as ZIP archives. Activate ‘photorec_win.exe’ and select a media. This can be external media such as USB-stick or SD-card. Confirm by choosing ‘Proceed’. Next, select the type of partition table generally ‘Intel’. In the next view, mark the drive and click ‘Search’ to start the search. Automatically the tool will restore deleted files and save them in the ‘recup_dir’ folder. This folder is under the photorec_win.exe program directory. This app is very useful whenever you accidentally delete your photo or other files. You can also recover USB or Memory Card using this application.
How to Use PhotoRec
- First, download the TeskDisk so you can use this restoring photo app.
- Then Extract then open the Testdisk folder
- Then select the win folder where there are testdisk.exe and photo_rec.exe
- Right-click the software and select Run Administrator, then a window will appear:
- Then press enter on “Proceed” will appear:
- Select your photos or another file
- If you use Windows then choose “Intel”:
- Select the photo that we want to recover.
- Then Select File System that matches your PC’s operating system if Windows uses the “Other options”, then Click Enter.
- Then choose “Free” or “Whole” as you wish, and click Enter to continue the process. Free is for files that are not WinRAR (mixed). Meanwhile, “Whole” is for files that are in the form of WinRAR
- Select the date where you deleted the file, then you press enter.
- Wait until the process is complete. We can see the file we are recovering where you extract in this app folder.
- After rebooting, the missing photos will reappear in Disk Management because you have used the [“Write” partition table function.
If you experience other damage such as the folder you are looking for does not exist or PhotoRec does not find a lost photo, there is a possibility of other damage on the hard disk.
Download PhotoRec Latest Version
- Download PhotoRec for Windows 32-bit – Download
- Download PhotoRec for Windows 64-bit – Download
- Download PhotoRec for Mac – Download
- Download PhotoRec for Linux 32-bit – Download
- Download PhotoRec for Linux 64-bit – Download
| Developer(s) | Christophe Grenier |
|---|---|
| Initial release | April 30, 2002; 17 years ago |
| Stable release | 7.1 / July 7, 2019; 3 months ago |
| Repository | git.cgsecurity.org/cgit/testdisk/ |
| Written in | C (nCurses) |
| Operating system | Cross-platform |
| Platform | CLI |
| Type | Data recovery |
| License | GNU GPL v2+ (free software) |
| Website | cgsecurity.org/wiki/PhotoRec |
PhotoRec is a free and open-sourceutility software for data recovery with text-based user interface using data carving techniques, designed to recover lost files from various digital camera memory, hard disk and CD-ROM. It can recover the files with more than 480 file extensions (about 300 file families).[1] It is also possible to add custom file signature to detect less known files.[2]
PhotoRec does not attempt to write to the damaged media the user is about to recover from. Recovered files are instead written to the directory from which PhotoRec is run, any other directory may be chosen. It can be used for data recovery or in a digital forensics context.[3][4][5][6][7]PhotoRec is shipped with TestDisk.[8]
PhotoRec is compatible with:[9]
- DOS (either real or in a Windows 9x DOS box)
- Microsoft Windows: NT4, 2000, XP, 2003, 2008, Vista, Windows 7
- FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD
Functionality[edit]
FAT, NTFS, ext2/ext3/ext4 filesystems store files in data blocks (also called data clusters under Windows). The cluster or block size remains at a constant number of sectors after being initialized during the formatting of the filesystem. In general, most operating systems try to store the data in a contiguous way so as to minimize data fragmentation. The seek time of mechanical drives is significant for writing and reading data to/from a hard disk, so that is why it is important to keep the fragmentation to a minimum level.
When a file is deleted, the meta-information about this file (filename, date/time, size, location of the first data block/cluster, etc.) is lost; e.g., in an ext3/ext4 filesystem, the names of deleted files are still present, but the location of the first data block is removed. This means the data is still present on the filesystem, but only until some or all of it is overwritten by new file data.
To recover these 'lost' files, PhotoRec first tries to find the data block (or cluster) size. If the filesystem is not corrupted, this value can be read from the superblock (ext2/ext3/ext4) or volume boot record (FAT, NTFS). Otherwise, PhotoRec reads the media, sector by sector, searching for the first ten files, from which it calculates the block/cluster size from their locations. Once this block size is known, PhotoRec reads the media block by block (or cluster by cluster). Each block is checked against a signature database; which comes with the program and has been growing in the type of files it can recover ever since PhotoRec's first version came out. It is a common data recovery method called file carving.
For example, PhotoRec identifies a JPEG file when a block begins with:
Photorec Software For Mac
- Start Of Image + APP0: 0xff, 0xd8, 0xff, 0xe0
- Start Of Image + APP1: 0xff, 0xd8, 0xff, 0xe1
- or Start Of Image + Comment: 0xff, 0xd8, 0xff, 0xfe
If PhotoRec has already started to recover a file, it stops its recovery, checks the consistency of the file when possible and starts to save the new file (which it determined from the signature it found).
If the data is not fragmented, the recovered file should be identical to (or possibly larger than) the original file in size. In some cases, PhotoRec can learn the original file size from the file header, so the recovered file is truncated to the correct size. If, however, the recovered file ends up being smaller than its header specifies, it is discarded. Some files, such as *.MP3 types, are data streams. In this case, PhotoRec parses the recovered data, then stops the recovery when the stream ends.
When a file is recovered successfully, PhotoRec checks the previous data blocks to see whether a file signature was found but the file was not able to be successfully recovered (i.e., the file was too small), and it tries again. This way, some fragmented files can be successfully recovered.[10]
Distribution[edit]
PhotoRec and TestDisk are shipped together. They can be downloaded from CGSecurity website.These utilities can be found on various LinuxLive CDs:
You can create different lists and add time-sensitive projects to them, create tasks with recurring due dates, and share your lists with others. You'll always be ready to take care of business. Wunderlist is the best task manager app you can get without paying for it. Numbers for mac free trial. It syncs across Mac and, so you can take your lists with you everywhere you go. There are dozens of pro-level tools, but they are designed to be used by anyone.See alsoProductivity Wunderlist.
- GParted Live CD [11]
- Parted Magic[12]
- Slax-LFI, a Slax-derived distribution [13]
- SystemRescueCD[14]
- Ubuntu Rescue Remix, an Ubuntu derivation [15]
They are also packaged for numerous *nix (mostly Linux based) distributions:
- ALT Linux[16]
- Arch Linux Extra Repository[17]
- Debian contrib[18]
- Fedora Extras[19]
- Red Hat Epel[20]
- FreeBSD port[21]
- OpenBSD port[22]
- Gentoo[23] and Gentoo Portage[24]
- Mandriva contrib
- Source Mage GNU/Linux[25]
- Ubuntu[26]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^[1].
- ^https://www.cgsecurity.org/wiki/Add_your_own_extension_to_PhotoRec
- ^Jack Wiles, Kevin Cardwell, Anthony Reyes (2007). The best damn cybercrime and digital forensics book period, p. 220. Syngress Publishing Inc. ISBN978-1-59749-228-7.
- ^Cameron H. Malin, Eoghan Casey, James M. Aquilina (2008). Malware Forensics: Investigating and Analyzing Malicious Code, p. xxviii. Syngress Publishing Inc. ISBN978-1-59749-268-3.
- ^Nathan Clarke (2010), Computer Forensics: A Pocket Guide, p. 67. IT Governance Publishing. ISBN978-1-84928-039-6.
- ^NIST Test Results for Graphic File Carving Tool: PhotoRec v7.0-WIP[permanent dead link].
- ^NIST Test Results for Video File Carving Tool: PhotoRec v7.0-WIPArchived 2015-04-22 at Archive.today.
- ^Scott Mueller, Brian Knittel (2008). Upgrading and Repairing Microsoft Windows, Second Edition, page 685. Pearson Education Inc. ISBN978-0-7897-3695-6.
- ^'PhotoRec - CGSecurity'. Retrieved March 1, 2013.
- ^How PhotoRec works (Description from the author website).
- ^'GParted -- Live CD/USB/PXE/HD'. Retrieved March 1, 2013.
- ^'programs – Parted Magic'. Archived from the original on January 2, 2011. Retrieved March 1, 2013.
- ^'Recover file with PhotoRec'. Archived from the original on May 2, 2013. Retrieved March 1, 2013.
- ^'System-tools - SystemRescueCd'. Retrieved March 1, 2013.
- ^'Software Ubuntu Rescue Remix'. Archived from the original on 2013-01-23. Retrieved March 1, 2013.
- ^TestDisk on ALT Linux
- ^ArchLinux Extra Repository
- ^TestDisk on Debian
- ^TestDisk in FedoraArchived 2011-03-10 at the Wayback Machine
- ^'RepoView: 'Fedora EPEL 6 - x86_64''. Archived from the original on 2015-09-13. Retrieved 27 July 2013.
- ^TestDisk in FreeBSD ports
- ^TestDisk in OpenBSD ports
- ^TestDisk in Gentoo
- ^TestDisk in Gentoo PortageArchived 2011-06-07 at the Wayback Machine
- ^TestDisk in Source MageArchived 2011-05-19 at the Wayback Machine
- ^[2]